# Consuming Semantic SQL endpoints
Starting from Ontopic Suite 2025.1.0
# Overview
Semantic SQL endpoints expose all data from the default graph of your knowledge graph through auto-generated virtual tables. These tables are organized into three distinct schemas:
classes: contains one table for each class in the knowledge graphdata_properties: contains one table for each property used as a data property in the knowledge graphobject_properties: contains one table for each property used as an object property in the knowledge graph
Class tables include as many relevant columns as possible while ensuring that the identifier column for each class instance serves as a primary key. These tables are denormalized by default to minimize the need for SQL users to deal with joins (see the corresponding parameter for more details). Since these are virtual tables, there's no performance penalty for including unused columns in your queries, thanks to Ontopic Suite's built-in optimizations.
What do we mean by semantic SQL?
Semantic SQL refers to queries expressed over the knowledge graph structure rather than the underlying data source structure. Ontopic Suite reformulates semantic SQL queries into source SQL queries that are executed directly by the data source.
# Foreign keys (beta)
Ontopic Suite automatically infers foreign keys between tables to recreate the linked data experience within SQL. This enables several powerful capabilities:
- Automatic generation of Entity-Relationship Diagrams using generic SQL tools (e.g., DBeaver)
- Table navigation features in clients like Metabase
- Enhanced SQL query generation by LLMs through better understanding of table relationships
This feature is currently in beta as some foreign keys may not be inferred in certain edge cases. Expect improved inference capabilities in upcoming releases.
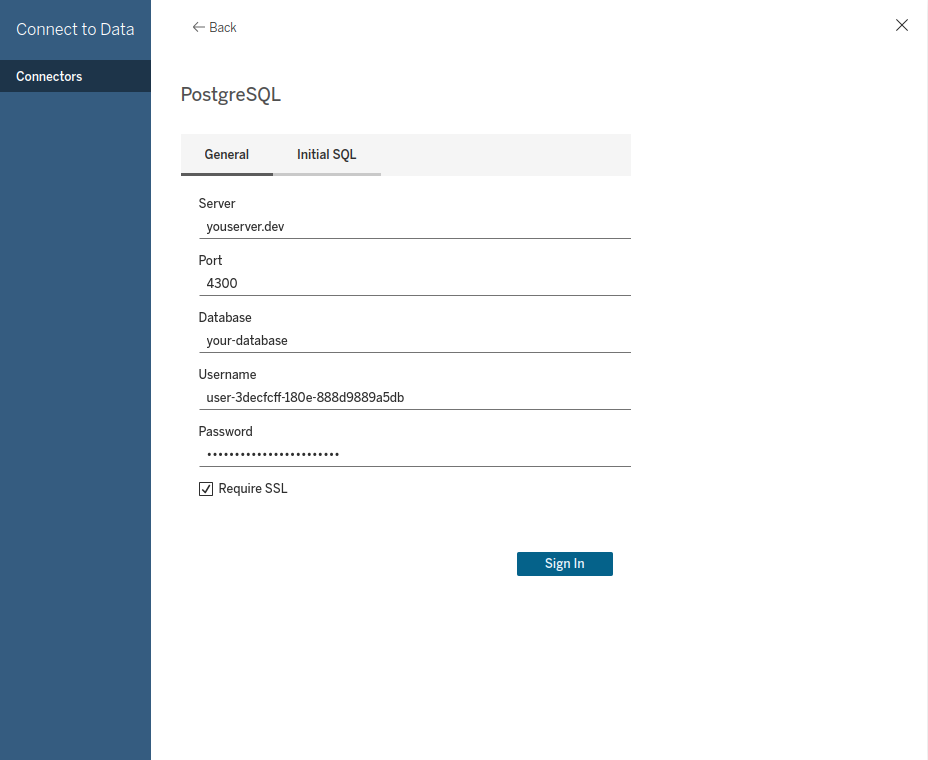
# Connecting to the PostgreSQL interface
You can find the connection details for the PostgreSQL interface on the Query > SQL page in Ontopic Suite's UI. To establish a connection, you'll need to:
- Create a Personal Access Token (used as the authentication password).
- Unless you are using the Windows Desktop distribution, download the CA certificate to secure TLS connections.
# Generic connection details
The PostgreSQL interface supports connections from various SQL clients, dashboarding tools, and BI platforms. Below are example connection details similar to those found on the Query > SQL page:
- Dialect:
PostgreSQL - Driver:
org.postgresql.Driver - Host:
yourserver.dev - Port:
4300 - Database:
your-database - Username:
user-3decfcff-180e-888d9889a5db - Access Token:
pwd-hMZffHW2skmaC8HGeBXg(to be generated in the UI)
Generally, a PostgreSQL connection string follows this format:
postgresql://<username>:<password>@<host>:<port>/<database>?key1=value1&key2=value2
For example, to connect to the example database using TLS:
postgresql://user-3decfcff-180e-888d9889a5db:pwd-hMZffHW2skmaC8HGeBXg@yourserver:4300/your-database?sslmode=verify-ca&sslrootcert=/path/to/ca.crt
Special characters in username or password
If there are special characters in the username or password (e.g., @, :, /, etc.), they must be percent-encoded (opens new window). For example, if the password is p@ss/w:rd, it should be encoded as p%40ss%2Fw%3Ard.
# TLS Security (not for Windows Desktop)
Ontopic Suite supports PostgreSQL sslmode values (opens new window) up to verify-ca for securing TLS connections. The verify-full mode is currently not supported because the certificate does not include the domain name and port.
When using verify-ca mode, you must provide the path to the Certificate Authority (CA) certificate using the sslrootcert parameter.
No TLS encryption for Windows Desktop
The Windows Desktop distribution is intended for local use, where TLS is not required.
# Supported clients
The PostgreSQL interface integrates with numerous SQL clients, business intelligence platforms, and data analysis tools. Here are some popular options with detailed configuration guides:
Example queries
All SQL queries used in this page are based on the knowledge graph from the quickstart guide.
# Power BI
Power BI (opens new window) is a business intelligence and data visualization platform that supports PostgreSQL connections through native drivers or ODBC.
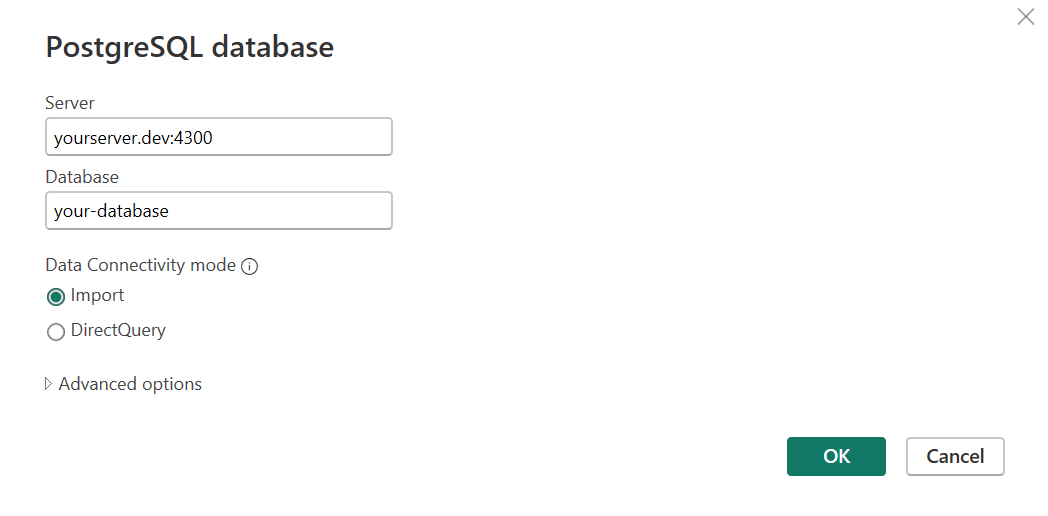
# Native Connection
Data can be consumed in two ways:
- Import mode: Data is imported into Power BI
- DirectQuery mode: Queries are executed directly on the data source without importing data
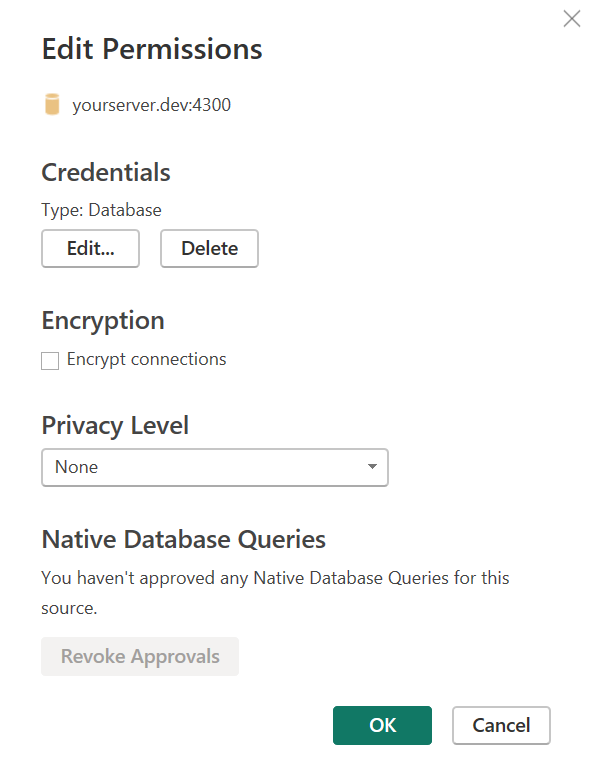
Disabling TLS for the native connection
Power BI requires the TLS certificate of native connections to be validated by a system-installed Certificate Authority. Unfortunately, at the moment you need to disable TLS.
If you are not using Windows Desktop, turn off encryption in the Power BI settings File > Options and settings > Data source settings > Edit Permissions and uncheck the Encrypt connections option.
# ODBC Connection
You can also connect using the psqlODBC (opens new window) driver. Note that ODBC connections only support import mode — direct querying is not available. For more information about ODBC connections, refer to the ODBC section.
# DBeaver
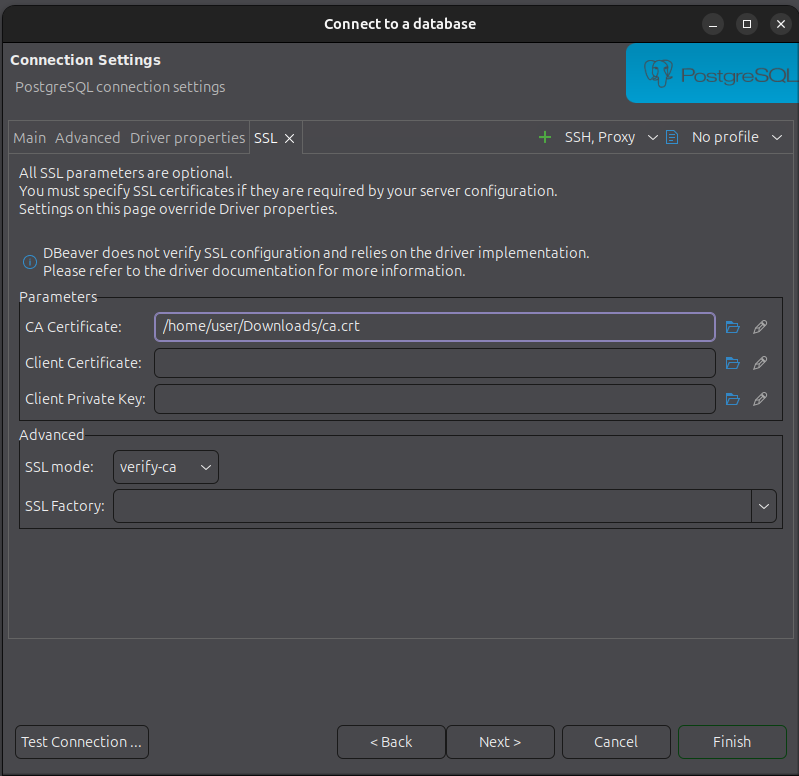
DBeaver (opens new window) is a free database management tool that supports connecting to PostgreSQL databases through JDBC drivers. It provides a visual interface to explore the database schema, run SQL queries, and manage database objects. You can use it to explore the data and generate Entity Relationship Diagrams.
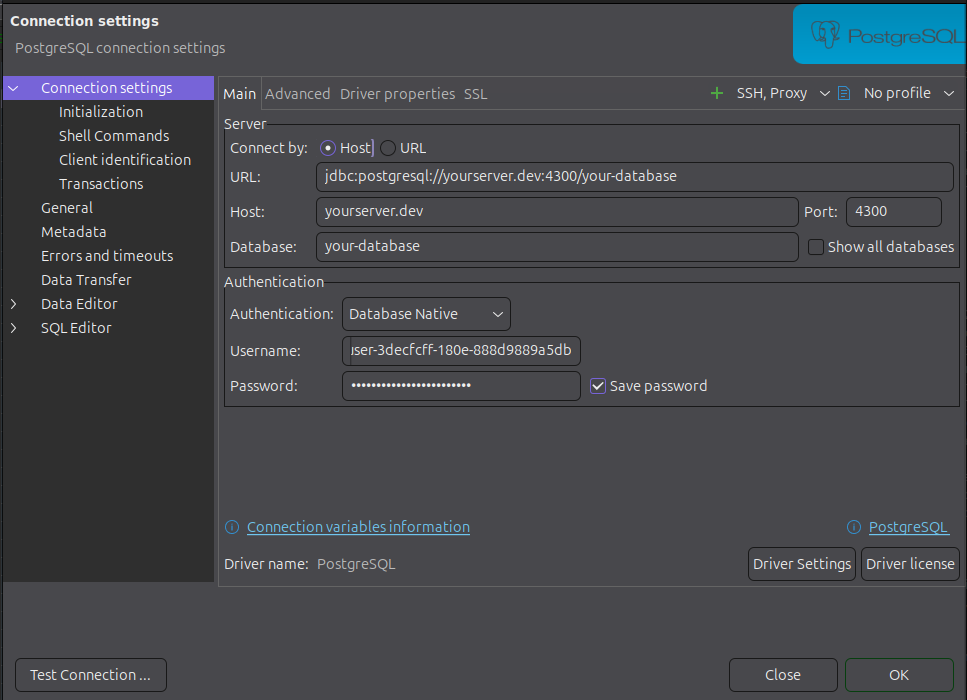
DBeaver also allows you to easily set up an TLS connection by specifying the mode and, if necessary, the path to the CA certificate. Please ignore this step for Windows Desktop.
# Tableau
Tableau (opens new window) is a visual analytics platform that connects to various data sources, including PostgreSQL databases. When creating a new Virtual Connection, you can configure each table as either:
- Live: Queries the data source directly (default)
- Extract: Imports data into Tableau's internal storage
Uncheck Require SSL for Windows Desktop.
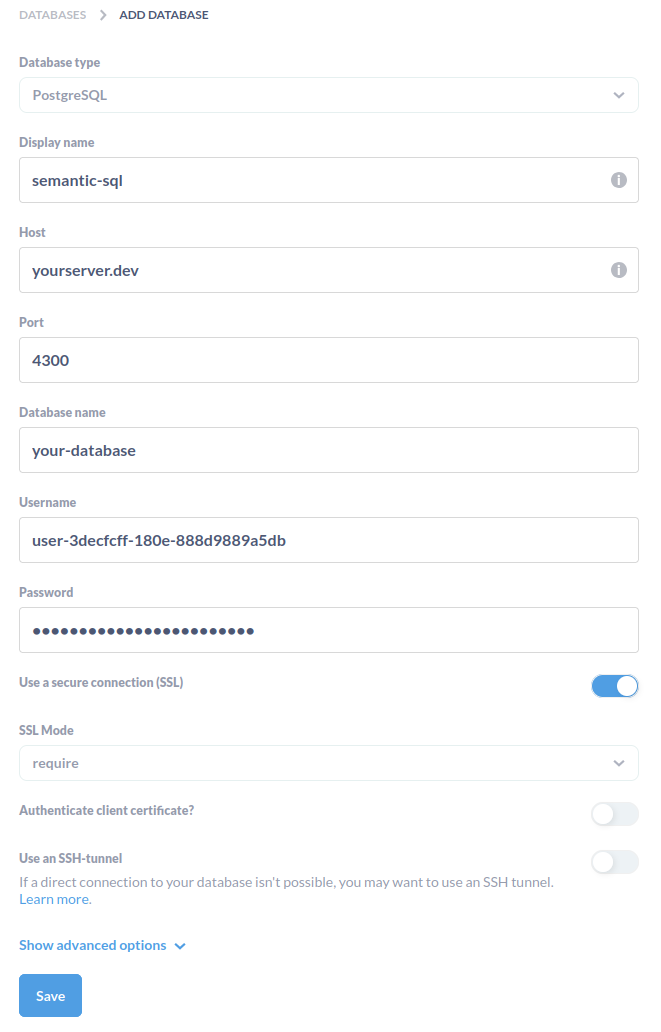
# Metabase
Metabase (opens new window) is an open-source business intelligence platform that supports PostgreSQL connections. Metabase leverages foreign key relationships to enable intuitive data exploration and automatic question suggestions.
Disable Use a secure connection (SSL) for Windows Desktop.
Incompatibility with latest versions
Metabase versions 0.51.0 and above are not currently supported by the semantic SQL endpoint. To use Metabase with Ontopic Suite, please install version 0.50.36 or earlier.
# Superset
Apache Superset (opens new window) is an open-source data exploration and visualization platform with native PostgreSQL support.
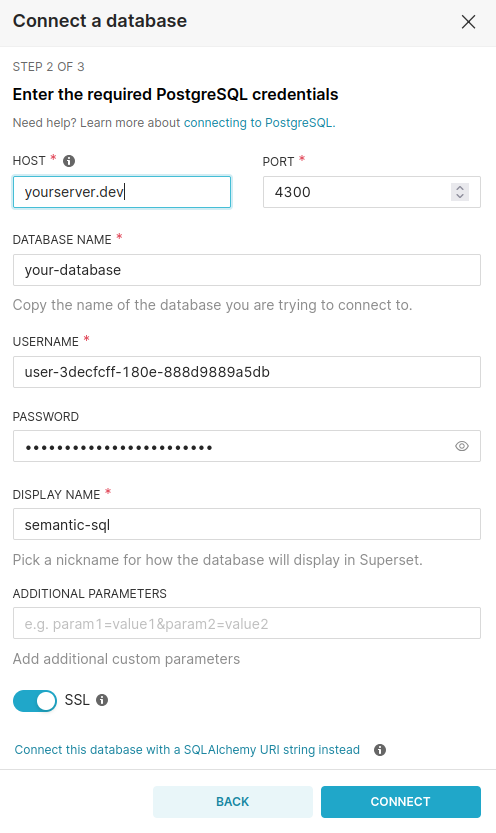
Note that the SSL checkbox in the connection page is equivalent to the sslmode=require option. Disable it for Windows Desktop. To use other SSL modes, you can specify them in the additional parameters field. For example, to use the verify-ca mode, you need the following parameters: sslmode=verify-ca&sslrootcert=/path/to/ca.crt.
# Excel
Microsoft Excel (opens new window) is a widely used spreadsheet application that allows users to import and analyze data from various sources, including PostgreSQL databases.
# ODBC Connection
To connect via ODBC, use the psqlODBC (opens new window) driver. For more information about ODBC connections, refer to the ODBC section.
To connect, go to Data > Get Data > From Other Sources > From ODBC in Excel and select the configured ODBC data source.
# Npgsql Connection
Npgsql (opens new window) is an open-source .NET data provider for PostgreSQL. To use it with Excel, Npgsql must be installed in the Global Assembly Cache (GAC). The easiest way to do this is through the Npgsql MSI installer (opens new window).
Once installed, you can connect by selecting Data > Get Data > From Database > From PostgreSQL Database in Excel and enter the connection details.
# Cube
Cube (opens new window) is a business intelligence semantic layer platform with powerful caching capabilities. It is commonly used for accelerating high-traffic dashboards where aggregations need to be pre-computed for optimal performance. Cube can connect to the PostgreSQL interface to create data cubes and serve them through its various interfaces.
While TLS settings cannot be configured through the Cube UI, you can set the necessary environment variables in your .env file to establish a secure connection. Below is an example configuration for enabling TLS and providing the CA certificate. If you are using Windows Desktop, please omit these settings.
CUBEJS_DB_SSL=true
CUBEJS_DB_SSL_CA=/path/to/ca.crt
As an alternative to the Docker image, Cube also offers a cloud-hosted solution that you can use to connect to the PostgreSQL interface.
# Model Context Protocol (MCP) Server
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) (opens new window) is an open protocol that standardizes how applications provide context to Large Language Models (LLMs). The MCP defines two roles:
- MCP Server: external resource (e.g., a database, API, file system, etc.) that provides context data through a set of tools that the LLM can invoke
- MCP Client: LLM application that requests context data from an MCP server to enhance its responses
In the context of Ontopic Suite, the PostgreSQL interface can act as a the datasource for an MCP server to provide information to the client. For example, you can use Claude Desktop (opens new window) as an MCP client and configure the claude_desktop_config.json file to define the MCP servers to connect to. Below is an example configuration to use the original Anthropic's PostgreSQL MCP server (opens new window) implementation, using the connection details to the PostgreSQL interface:
{
"mcpServers": {
"postgres": {
"command": "npx",
"args": [
"-y",
"@modelcontextprotocol/server-postgres",
"postgresql://user-3decfcff-180e-888d9889a5db:pwd-hMZffHW2skmaC8HGeBXg@yourserver:4300/your-database"
]
}
}
}
# ODBC
ODBC (opens new window) (Open Database Connectivity) is a standard API for accessing database management systems, allowing applications to connect to various databases using a common interface.
We recommend using the psqlODBC (opens new window) driver for connecting to PostgreSQL.
# Windows
For installing the driver on Windows, download the installer from the psqlODBC download page (opens new window) and follow the installation instructions.
Once the driver is installed, you can configure a new ODBC data source using the ODBC Data Source Administrator tool. Below is an example configuration:
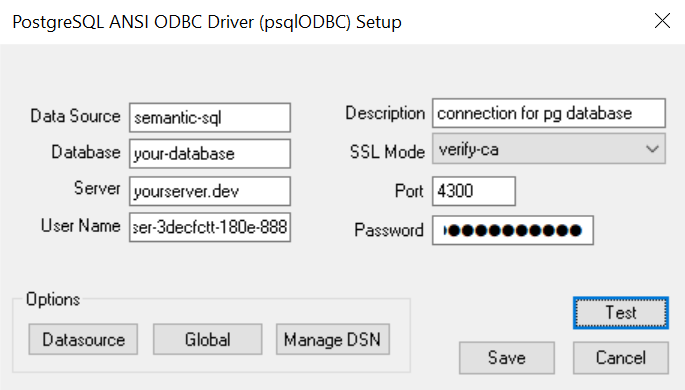
For Windows Desktop, set the SSL mode to disable. Otherwise, in order to use the verify-ca SSL mode, you'll need to add the CA certificate to the Users\<user>\AppData\Roaming\postgresql\ directory and name it root.crt.
# Linux
On Linux, install the psqlODBC driver using your package manager. For example, on Debian-based systems:
sudo apt-get install odbc-postgresql
After installation, configure a new ODBC data source by editing the odbc.ini file (typically located in /etc/ or your home directory):
[PostgreSQL]
Driver = PostgreSQL Unicode
Database = your-database
Servername = yourserver.dev
Port = 4300
Username = user-3decfcff-180e-888d9889a5db
Password = pwd-hMZffHW2skmaC8HGeBXg
SSLmode = verify-ca
SSLrootcert = /path/to/ca.crt
# JDBC
JDBC (opens new window) (Java Database Connectivity) is an API that enables Java applications to interact with databases, providing a standard interface for connecting to databases.
To connect to the PostgreSQL interface, use the PostgreSQL JDBC Driver (opens new window):
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String url = "jdbc:postgresql://yourserver.dev:4300/your-database";
String user = "user-3decfcff-180e-888d9889a5db";
String password = "pwd-hMZffHW2skmaC8HGeBXg";
String sslParams = "?sslmode=verify-ca&sslrootcert=/path/to/ca.crt";
try {
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url + sslParams, user, password);
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery("SELECT * FROM classes.\"LodgingBusiness\";");
while (rs.next()) {
System.out.println(rs.getString("name") + ", " + rs.getString("containedIn.name"));
}
rs.close();
stmt.close();
conn.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
If you are using Windows Desktop, please omit the sslParams variable.
# Python
The Python ecosystem offers several libraries to connect to PostgreSQL databases.
# Psycopg
Psycopg (opens new window) is a popular PostgreSQL adapter for Python.
import psycopg2
conn = psycopg2.connect(
dbname="your-database",
user="user-3decfcff-180e-888d9889a5db",
password="pwd-hMZffHW2skmaC8HGeBXg",
host="yourserver.dev",
port=4300,
sslmode='verify-ca',
sslrootcert="/path/to/ca.crt")
with conn.cursor() as cur:
cur.execute("SELECT * FROM classes.\"LodgingBusiness\";")
rows = cur.fetchall()
for row in rows:
print(row)
conn.close()
For Windows Desktop, you can omit the sslmode and sslrootcert parameters.
Server-side cursors not supported
Psycopg supports server-side cursors through the name parameter of the cursor() method. However, this feature is incompatible with the SQL endpoint. Use client-side cursors (the default behavior) for fetching query results.
# SQLAlchemy
SQLAlchemy (opens new window) is a SQL toolkit and Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) library for Python, providing a more-high level interface for interacting with databases.
from sqlalchemy import create_engine, text
engine = create_engine(
"postgresql+psycopg2://user-3decfcff-180e-888d9889a5db:pwd-hMZffHW2skmaC8HGeBXg@yourserver:4300/your-database",
connect_args={"sslmode": "verify-ca","sslrootcert": "ca.crt"}
)
with engine.connect() as conn:
result = conn.execute(text("SELECT * FROM classes.\"LodgingBusiness\";"))
for row in result:
print(row)
engine.dispose()
If you are using Windows Desktop, please omit the sslmode and sslrootcert parameters.
Alternatively, you can also use the ORM interface to map tables to Python classes, allowing you to define models and perform queries using Python objects.
from sqlalchemy import create_engine, Column, String, ForeignKey
from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base
from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker
Base = declarative_base()
class Municipality(Base):
__tablename__ = 'Municipality'
__table_args__ = {'schema': 'classes'}
id = Column("municipality_id", String, primary_key=True)
name = Column("name", String)
class LodgingBusiness(Base):
__tablename__ = 'LodgingBusiness'
__table_args__ = {'schema': 'classes'}
id = Column("lodgingBusiness_id",String, primary_key=True)
name = Column("name", String)
containedIn = Column("containedIn", String, ForeignKey("classes.Municipality.municipality_id"))
containedInName = Column("containedIn.name", String)
engine = create_engine(
"postgresql+psycopg2://user-3decfcff-180e-888d9889a5db:pwd-hMZffHW2skmaC8HGeBXg@yourserver:4300/your-database",
connect_args={"sslmode": "verify-ca","sslrootcert": "ca.crt"}
)
session = sessionmaker(bind=engine)()
results = session.query(LodgingBusiness).filter(LodgingBusiness.containedInName == 'Bolzano/Bozen').all()
for row in results:
print(row.name, row.containedInName)
If you are using Windows Desktop, please omit the sslmode and sslrootcert parameters.
SQLAlchemy reflection not supported
SQLAlchemy's table reflection feature, which automatically introspects database schema information (columns, data types, foreign keys, etc.) to build Table objects, is not supported by the semantic SQL endpoint. Instead, you must explicitly define the table structure in your Python code, including all columns and their data types, as demonstrated in the ORM example above.
# Pandas
Pandas (opens new window) is a powerful data manipulation and analysis library for Python. It provides data structures like DataFrames that make it easy to work with structured data such as SQL query results. Pandas can connect to PostgreSQL databases using SQLAlchemy.
import pandas as pd
from sqlalchemy import create_engine, text
engine = create_engine(
"postgresql+psycopg2://user-3decfcff-180e-888d9889a5db:pwd-hMZffHW2skmaC8HGeBXg@yourserver:4300/your-database",
connect_args={"sslmode": "verify-ca","sslrootcert": "ca.crt"}
)
with engine.connect() as conn:
df = pd.read_sql(text("SELECT * FROM classes.\"LodgingBusiness\";"), conn)
print(df.head())
engine.dispose()
For Windows Desktop, please omit the sslmode and sslrootcert parameters.
Alternatively, you can also consume the data in chunks. Note however, that the query results are fully retrieved in memory and only afterwards split into chunks.
import pandas as pd
from sqlalchemy import create_engine, text
engine = create_engine(
"postgresql+psycopg2://user-3decfcff-180e-888d9889a5db:pwd-hMZffHW2skmaC8HGeBXg@yourserver:4300/your-database",
connect_args={"sslmode": "verify-ca","sslrootcert": "ca.crt"}
)
with engine.connect() as conn:
for chunk in pd.read_sql(text("SELECT * FROM classes.\"LodgingBusiness\";"), conn, chunksize=1000):
print(chunk.head())
engine.dispose()
For Windows Desktop, please omit the sslmode and sslrootcert parameters.
# Polars
Polars (opens new window) is a fast DataFrame library implemented in Rust, with Python bindings available. It provides efficient data manipulation and analysis capabilities, similar to Pandas, but optimized for performance.
import polars as pl
from sqlalchemy import create_engine, text
engine = create_engine(
"postgresql+psycopg2://user-3decfcff-180e-888d9889a5db:pwd-hMZffHW2skmaC8HGeBXg@yourserver:4300/your-database",
connect_args={"sslmode": "verify-ca","sslrootcert": "ca.crt"}
)
with engine.connect() as conn:
df = pl.read_sql(text("SELECT * FROM classes.\"LodgingBusiness\";"), conn)
print(df)
If using Windows Desktop, please omit the sslmode and sslrootcert parameters.
No support for parameterized queries
Unlike the other libraries covered in this documentation, Polars does not support parameterized queries directly. To work around this limitation, you can leverage SQLAlchemy to safely construct parameterized query strings and then pass the compiled SQL to Polars.
import polars as pl
from sqlalchemy import create_engine, text
engine = create_engine("postgresql+psycopg2://user-3decfcff-180e-888d9889a5db:pwd-hMZffHW2skmaC8HGeBXg@yourserver:4300/your-database")
with engine.connect() as conn:
municipality_name = 'Bolzano/Bozen'
query = text("SELECT * FROM classes.\"LodgingBusiness\" WHERE \"containedIn.name\" = :name;")
compiled = query.bindparams(name=municipality_name).compile(compile_kwargs={"literal_binds": True})
sql = str(compiled)
df = pl.read_database(sql, conn)
print(df)
No support for read_database_uri()
In addition to the read_database function, Polars offers a read_database_uri function that accepts database connection strings directly. However, this function is incompatible with the semantic SQL endpoint because it depends on ConnectorX or ADBC engines, neither of which are supported. Use the read_database function with an established connection object instead.
# PyTorch
PyTorch (opens new window) is a popular open-source machine learning framework for Python, widely used for deep learning applications. Although PyTorch doesn't include native PostgreSQL connectivity, you can integrate it with database libraries like Psycopg or SQLAlchemy to fetch data and create a custom PyTorch Dataset.
import psycopg2
import torch
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
class PostgresDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, rows):
conn = psycopg2.connect(
host="yourserver.dev",
port=4300,
database="your-database",
user="user-3decfcff-180e-888d9889a5db",
password="pwd-hMZffHW2skmaC8HGeBXg",
sslmode='verify-ca',
sslrootcert="/path/to/ca.crt"
)
cursor = conn.cursor()
rows = cursor.execute("""SELECT \"feat1\", \"feat2\", ..., \"featN\", label FROM dataset;""").fetchall()
cursor.close()
conn.close()
self.features = torch.tensor([row[:-1] for row in rows], dtype=torch.float32)
self.labels = torch.tensor([row[-1] for row in rows], dtype=torch.long)
def __len__(self):
return len(self.features)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
return self.features[idx], self.labels[idx]
dataset = PostgresDataset(rows)
dataloader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=32, shuffle=True)
for batch_features, batch_labels in dataloader:
# Use batch_features and batch_labels for training your model
pass
For Windows Desktop, please omit the sslmode and sslrootcert parameters.
# R
R (opens new window) is a programming language and environment specifically designed for statistical computing and data analysis. R integrates with PostgreSQL through the RPostgres and DBI packages.
library(DBI)
library(RPostgres)
con <- dbConnect(
RPostgres::Postgres(),
dbname = "your-database",
host = "yourserver.dev",
port = 4300,
user = "user-3decfcff-180e-888d9889a5db",
password = "pwd-hMZffHW2skmaC8HGeBXg",
sslmode = 'verify-ca',
sslrootcert = "/path/to/ca.crt"
)
df <- dbGetQuery(con, "SELECT * FROM classes.\"LodgingBusiness\";")
print(head(df))
dbDisconnect(con)
For Windows Desktop, please omit the sslmode and sslrootcert parameters.
R also makes it easy to work with large datasets using the dbFetch function, which retrieves query results in chunks.
library(DBI)
library(RPostgres)
con <- dbConnect(
RPostgres::Postgres(),
dbname = "your-database",
host = "yourserver.dev",
port = 4300,
user = "user-3decfcff-180e-888d9889a5db",
password = "pwd-hMZffHW2skmaC8HGeBXg",
sslmode = 'verify-ca',
sslrootcert = "/path/to/ca.crt"
)
res <- dbSendQuery(con, "SELECT * FROM classes.\"LodgingBusiness\";")
while (!dbHasCompleted(res)) {
chunk <- dbFetch(res, n = 1000)
print(head(chunk))
}
dbClearResult(res)
dbDisconnect(con)
For Windows Desktop, please omit the sslmode and sslrootcert parameters.
No support for parameterized queries
Although R supports parameterized queries through the dbBind function, this feature is currently incompatible with the semantic SQL endpoint. As a workaround, construct SQL queries as strings.
library(DBI)
library(RPostgres)
con <- dbConnect(
RPostgres::Postgres(),
dbname = "your-database",
host = "yourserver.dev",
port = 4300,
user = "user-3decfcff-180e-888d9889a5db",
password = "pwd-hMZffHW2skmaC8HGeBXg",
sslmode = 'verify-ca',
sslrootcert = "/path/to/ca.crt"
)
name <- 'Bolzano/Bozen'
query <- paste(
"SELECT * FROM classes.\"LodgingBusiness\" WHERE \"containedIn.name\" = ", dbQuoteLiteral(con, name)
)
df <- dbGetQuery(con, query)
print(head(df))
dbDisconnect(con)
# Query Reformulation
Semantic SQL queries can be fully reformulated into source SQL queries optimized for execution by your data source. The reformulated queries preserve the same column names and data types as the original semantic queries.
This capability enables several advanced use cases:
- Pure reformulation service: Use the Web API to generate optimized source queries without routing data through the semantic endpoint
- Design-time knowledge graphs: Use the knowledge graph for query design, then execute predefined queries at runtime for optimal performance
This capability is particularly valuable when working with large datasets, as it reduces network overhead and eliminates intermediate data transformations.
# Configuration parameters
Configuration parameters can be set in Settings > SQL Configuration entries.
# Auto-generated column depth
The parameter autogeneratedColumnDepth controls the level of denormalization of class tables.
With its default value of 1, properties of resources one step away are also added as columns in the class table.
For instance, the class table Hotel includes the column geo.latitude, which corresponds to the latitude of the GeoCoordinate instance linked to the hotel through the object property geo. With autogeneratedColumnDepth set to 0, only direct properties of hotels (e.g., name, geo and city) are included as columns. With the value set to 2, it includes columns like city.state.name for the name of the state where the hotel's city is located.
For clean Entity-Relationship Diagrams generated by SQL tools like DBeaver, we recommend setting this value to 0. For usage in BI tools like Tableau and Power BI, we recommend setting it to 1 or 2 to save users from handling joins themselves.